Beetroots, or beets, have risen in popularity now that researchers have identified links between drinking beetroot juice and lowered blood pressure, reduced inflammation, and improved athletic performance.
Beetroots have an excellent nutritional profile that includes plenty of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They also contain unique bioactive compounds called betalains, which may benefit a person’s health.
People can get these benefits from consuming whole beetroots or their juice.
In this article, we look at the research behind six proposed health benefits of beetroot juice. We also cover dosage and how to make the juice at home.
1. Good nutritional profile
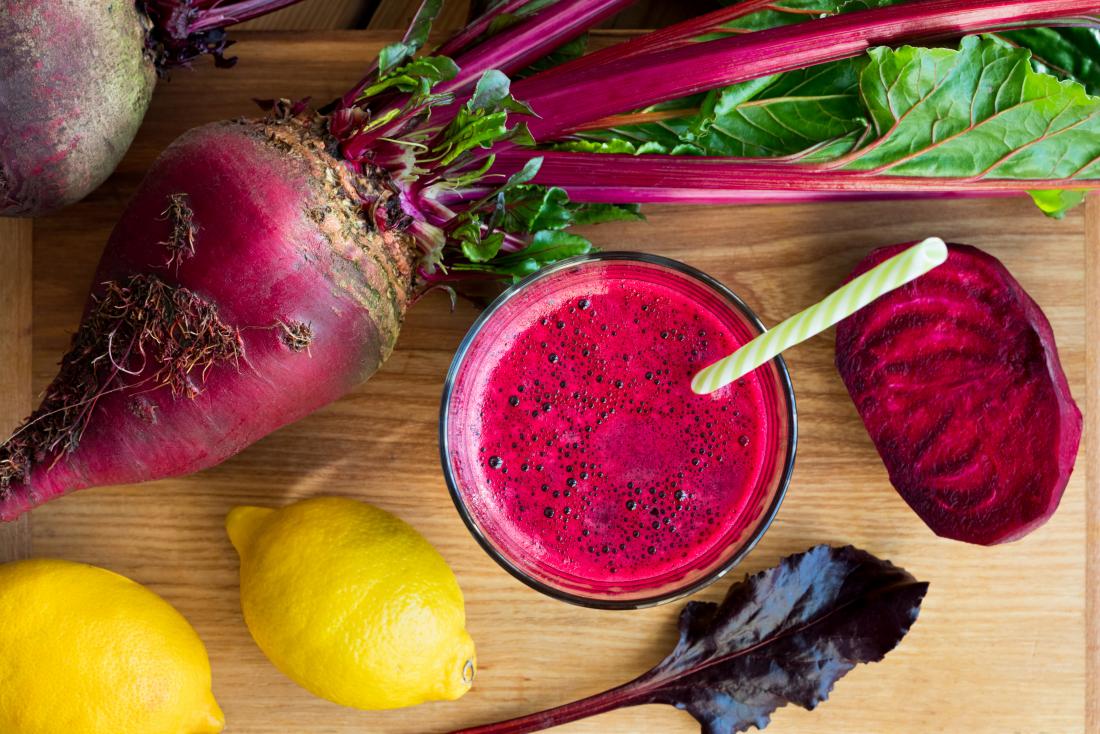

Beetroot juice is rich in a range of nutrients.
Beetroot juice contains a wide range of essential vitamins and minerals. Drinking this vegetable juice regularly can help prevent deficiencies in these nutrients.
A 100-milliliter (ml) serving of organic beetroot juice, which is equivalent to a small glass, contains 29 calories, no fat, and the following nutrients:
- 0.42 grams (g) of protein
- 7.50 g of carbohydrates
- 5.42 g of sugar
- 0.40 g of fiber
Beetroot juice also contains antioxidants. Antioxidants reduce oxidative stress, which research has linked to the development of cancer, inflammatory conditions, and heart disease.
Beetroots are a rich source of essential vitamins and minerals, including:
- folate, which is important for DNA and cell health
- vitamin C, an antioxidant that plays a role in wound healing and immune system function
- vitamin B-6, which supports metabolism and red blood cell production
- calcium, an essential mineral for bone growth and strength
- iron, which allows red blood cells to carry oxygen
- magnesium, a mineral that supports immune, heart, muscle, and nerve health
- manganese, which contributes to the regulation of metabolism and blood sugar levels
- phosphorous, an essential nutrient for teeth, bones, and cell repair
- copper, which plays a role in making collagen, maintaining bones and blood vessels, and supporting immune function
- zinc, which promotes wound healing, supports the immune system, and encourages normal growth
Beetroots also contain other beneficial compounds:
- Phytochemicals give plants their color and flavor. They also stimulate the immune system, minimize inflammation, and reduce oxidative stress.
- Betalains are responsible for the deep red color of beetroots. These pigments have promising antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antitoxic properties.
- Nitrates refer to a group of organic compounds that improve blood flow and promote heart health.
2. Improving blood pressure
A growing body of research suggests that beetroots can help lower a person’s blood pressure. Researchers believe that this is due to their nitrate content.
Beets naturally contain large quantities of nitrates, which the body converts into nitric oxide. This compound dilates the blood vessels, which improves blood flow and lowers overall blood pressure.
In a recent study, researchers gave participants 70 ml of either nitrate-rich beetroot juice or a nitrate-depleted placebo juice. The blood pressure of those in the test group decreased by 5.2 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) more than that of those in the placebo group after just 30 minutes. However, the effect of the concentrated beetroot juice subsided within 24 hours.
Another small-scale study showed that drinking 250 ml of beetroot juice every day for 4 weeks lowered blood pressure among people with hypertension.
However, people who are already taking medication to lower their blood pressure may not notice the same benefits. The findings of a 2015 study involving people who were taking blood pressure medications revealed that nitrate-rich beetroot juice did not lower blood pressure after 1 week compared with nitrate-depleted beetroot juice.
3. Reducing inflammation
Beetroot juice contains anti-inflammatory compounds called betalains.
According to a 2015 review, betalains inhibit specific signaling pathways that play a role in inflammatory diseases.
A 2014 study showed that a betalain called phenethylamine-betaxanthin reduced the activity of an inflammatory enzyme by 32 percent.
4. Preventing anemia

Anemia can cause headaches and fatigue.
Beetroots are rich in iron, an essential component of red blood cells. Without iron, red blood cells cannot transport oxygen around the body.
People who have low iron levels can sometimes develop a condition called iron deficiency anemia. Adding sources of iron to the diet can reduce the risk of this condition.
The symptoms of iron deficiency anemia include:
5. Protecting the liver
Beetroot juice contains antioxidants, vitamin A, vitamin B-6, and iron. These compounds help protect the liver from inflammation and oxidative stress while enhancing its ability to remove toxins from the body.
A recent small-scale animal study in rats with liver injury found that the rodents that received a beetroot extract had minimal liver damage in comparison with control rats.
6. Boosting athletic performance
Certain compounds in beetroot juice, such as nitrates and betalains, may improve athletic performance.
According to a 2017 systematic review, nitrates can boost a person’s athletic efficiency by increasing blood flow and oxygen to the muscles.
A 2018 study looked at the effects of betalain on 28 trained male cyclists. The cyclists received 100 mg of either beetroot concentrate or placebo every day for a week. Compared with the placebo group, the beetroot concentrate group had higher exercise efficiency and increased blood flow.
Dosage
Currently, there are no official dosage recommendations for beetroot juice.
According to a 2014 study, drinking one 250-ml glass of beetroot juice per day may lower blood pressure. The juice did not cause any serious side effects, but the participants did report a change in the color of their urine.
The authors noted that the ability of beetroot juice to lower blood pressure depends on the nitrate concentration, which can vary widely among different beetroot juices. The authors recommend a concentration of 4 millimoles per liter (mmol) of nitrate to lower blood pressure in healthy adults.
Side effects

A person with low blood pressure should avoid drinking beetroot juice regularly.
In most cases, people can safely eat beets or drink beetroot juice without experiencing any negative side effects.
Drinking beetroot juice regularly can affect the color of urine and feces due to the natural pigments in beets. People may notice pink or purple urine, which is called beeturia, and pink or purple feces. These color changes are temporary and not a cause for concern.
The nitrates in beetroot juice affect blood pressure. Anyone who has low blood pressure or is currently taking blood pressure medication should speak with a healthcare professional before adding beets or beetroot juice to their diet.
Beets contain high levels of oxalates, which can cause kidney stones in people with a high risk of this condition.
How to make beetroot juice
People can make beetroot juice at home using a juicer, blender, or food processor.
How to prepare the beets:
- Trim the tops off the beets before washing them thoroughly. Leave the beetroot skin intact for extra nutrients.
- Chop the beets into small pieces.
How to juice the beets:
- Set up a juicer with a bowl or pitcher in position to catch discarded material.
- Feed the beetroot pieces into the juicer one at a time.
- Pour the beetroot juice into a glass, and immediately drink it or place it in the refrigerator to chill.
How to blend the beets:
- Place the beetroot pieces into the blender, and add a splash of water to help soften up the beetroot.
- Blend until smooth.
- Remove large chunks from the juice using a cheesecloth or fine-mesh strainer.
- Discard the pulp and pour the beetroot juice into a glass. Chill it in the refrigerator or serve it straight away.
People can drink beetroot juice on its own, or they can blend it with the juice of other fruits and vegetables.
The following healthful ingredients can add a flavorful twist:
People can also buy beetroot juice from their local grocery store or choose between brands online.
It is important to check the nutrition label on products and avoid juices that contain added sugars and preservatives.
Summary
Beetroots are a healthful addition to most diets. People can experience the health benefits of beetroots by eating them raw or cooked or by drinking beetroot juice. Juiced beets contain many beneficial nutrients that the cooking process can remove.