As people get older, their hair may start to lose volume and thickness. In some cases, thinning hair is linked with diet, nutrient deficiencies, or hereditary hair loss.
In most cases, thinning hair is not linked with overall health concerns. However, it can affect people’s mental health and self-esteem.
People can try several treatments and home remedies to boost hair health, thickness, and strength.
In this article, we look at the causes of thinning hair, as well as some of the treatments and home remedies available.
Causes
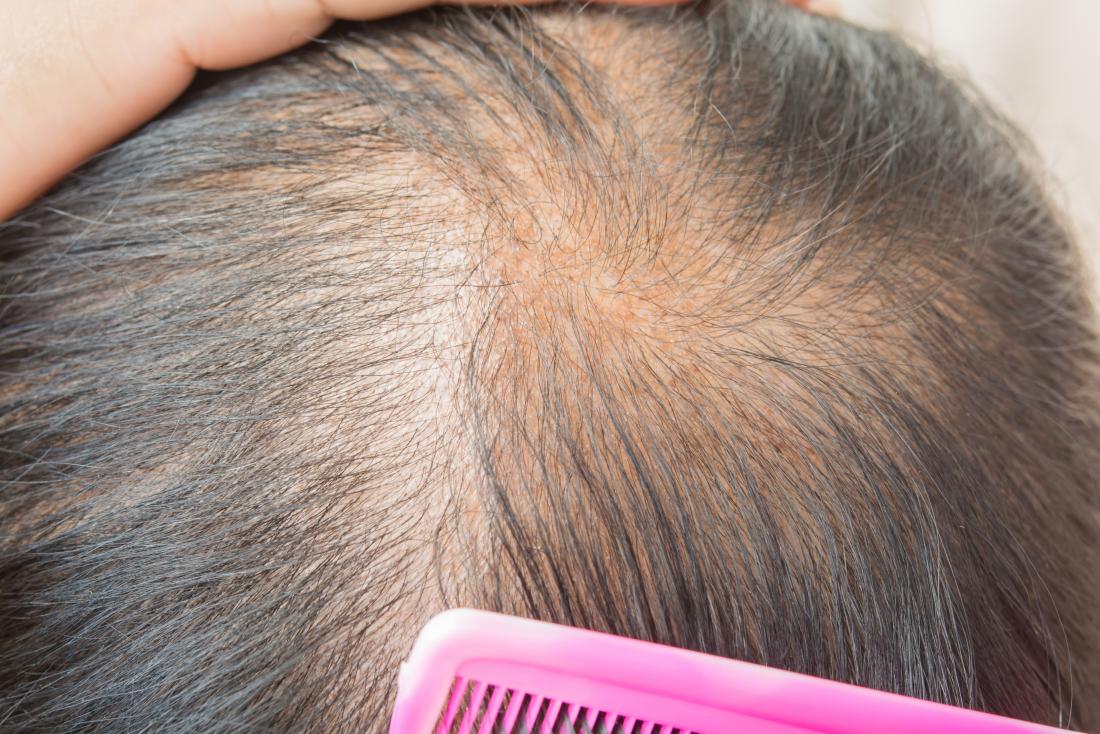 As people get older, experiencing some degree of hair loss is normal.
As people get older, experiencing some degree of hair loss is normal.Some degree of hair loss is normal. As people get older, their hair may naturally start to lose volume and strength.
The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) point out that people lose 50–100 hairs each day. New hair then regrows from the same hair follicles.
Over time, however, some follicles stop producing hair, and hair shafts become finer. The hair also starts to lose its color.
If a person notices significant hair thinning or the development of bald patches, they may be experiencing hair loss. According to the ADD, people can stop or treat most causes of hair loss.
The following sections look at possible causes of thinning hair.
Male or female pattern hair loss
Male pattern baldness and female pattern baldness are together called androgenetic alopecia. Genes and hormones cause androgenetic alopecia.
Androgenetic alopecia is a frequent cause of hair loss. It affects an estimated 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States.
According to the Genetics Home Reference, the likelihood of experiencing androgenetic alopecia increases with age. Although it can affect teenagers, over half of males aged 50 and older have some degree of hair loss. It is most likely to affect females following menopause.
Often, people who have androgenetic alopecia have family members with the same condition.
In males, hair thinning tends to occur from the hairline to the back of the head. In females, it tends to affect the crown of the head.
Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is a condition that causes hair loss in round patches on the scalp. It can also affect the eyebrows, beard, and other areas where hair is present.
People in the U.S. have a 2.1% chance of developing alopecia areata in their lifetime. It often occurs during childhood. Genes and environmental factors are the main causes.
In alopecia areata, the hair follicles are still alive, and the hair can regrow. Doctors may treat alopecia areata with an injection into the scalp every 4–6 weeks for up to 6 months.
Diet
The body needs nutrients in order to create new hair strands and maintain healthy hair follicles.
Protein is an essential component of hair. Micronutrients, which include vitamins and minerals, play a key role in the hair follicle growth cycle.
Malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies can cause hair loss. Eating a healthful, varied diet can help promote the continued growth of strong, healthy hair.
Eating a nutritious diet can also prevent the following signs of damaged hair:
- brittle hair shafts
- a dull appearance
- dryness
- dandruff
Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D stimulates the hair follicles, resulting in hair growth. When a person does not get enough vitamin D, they may experience hair loss, alongside other symptoms.
Some research has linked vitamin D deficiencies with alopecia areata.
Learn about vitamin D deficiency and hair loss.
Stress
After a long period of significant stress, people may notice that their hair feels thinner than usual. This is called telogen effluvium.
When stress causes thinning hair, people usually notice their hair returning to its normal volume once the stressful situation begins to pass.
Healthcare professionals can help people manage significant times of stress. Talking and behavioral therapies can help. People can also try natural remedies for dealing with stress and anxiety.
Pregnancy
People may notice hair loss during or after pregnancy. Typically, the hair grows back without any treatment.
Treatment
People can try taking prescription medication to treat thinning hair.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have officially approved two prescription drugs for treating androgenetic alopecia: minoxidil and finasteride.
Minoxidil
Minoxidil comes in 2% and 5% treatments. People apply the product directly to the areas of thinning hair.
This is a safe and effective treatment for androgenetic alopecia.
It takes 6–12 months for hair growth to improve. However, people taking minoxidil will have to keep taking it permanently, or hair loss will reoccur.
Side effects of taking minoxidil can include:
- contact dermatitis
- skin irritation
- excessive hair growth
Finasteride
Finasteride (Propecia) is an oral medication. People experiencing hair loss take 1 milligram daily. This is a prescription drug for men who have already tried minoxidil without success.
Side effects of taking finasteride can include:
Home remedies
 Eating eggs may boost hair growth.
Eating eggs may boost hair growth.People can also try a range of home remedies to improve hair growth.
However, not all home remedies have scientific backing. For this reason, people should speak with a doctor before trying any new home remedy for hair loss.
Studies into natural treatments are numerous and show promise. However, herbal remedies do not currently have FDA approval, and more research is needed to confirm their benefits.
The following sections look at home remedies that people can try to treat thinning hair.
Eat hair-healthy foods
Diet plays an important role in the strength and health of a person’s hair. Proteins, fats, and certain vitamins and minerals are especially important for hair health.
People may notice improvements in hair growth when they increase the amount of certain foods in their diet.
Foods that may boost hair growth include:
- Eggs: These contain protein, which is essential for hair growth. They also contain biotin, a B vitamin that may boost hair growth, though research results are mixed.
- Brazil nuts: These are a source of selenium, a mineral that may improve hair health.
- Fatty fish: This is a good source of omega-3, which may also improve hair growth.
- Walnuts: These also contain omega-3.
Get more vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiencies can contribute to hair loss. Addressing this deficiency could improve thinning hair.
People get most of their vitamin D from exposure to sunlight and their diet. Foods high in vitamin D include:
- fatty fish
- beef liver
- cheese
- egg yolks
- mushrooms
- fortified foods, such as milks, cereals, and juices
Try essential oils
Some people use essential oils to boost hair growth. There has been little research into how effective these oils can be, but they are unlikely to be harmful.
When using essential oils, people should always dilute them in a carrier oil such as coconut oil or jojoba oil to avoid irritation. Learn more about carrier oils here.
Aromatherapy practitioners may use the following oils to boost hair growth:
Rosemary oil
Some animal studies have suggested that rosemary oil may increase blood flow and could therefore improve scalp health. A healthy scalp is important for healthy hair growth.
One 2015 trial compared rosemary oil with minoxidil 2%. After 6 months, the participants applying rosemary oil and those applying topical minoxidil both experienced significant hair growth.
Peppermint oil
Also capable of stimulating blood circulation, peppermint oil has shown promise as a treatment for thinning hair.
In a 2014 animal study, scientists found that compared with treatments using salt water, jojoba oil, and minoxidil 3%, those using peppermint oil led to the most hair growth over 4 weeks.
They measured hair growth by assessing using hair thickness, follicle number, and follicle depth.
Other oils
Some people also use the following oils for hair growth:
- cedarwood
- lavender oil
- tulsi oil
- thyme oil
- Scalp massage
Massaging the scalp may help promote blood flow. This, in turn, may encourage hair to grow. Performing a gentle scalp massage using essential oils could provide extra benefits.
Other natural remedies
According to a 2019 review of alternative treatments for alopecia, the following remedies could also help with hair growth:
- capsaicin, a compound present in red chili peppers
- ginseng, an herb with traditional use as a hair loss remedy
- garlic gel, due to its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties
- onion juice, which may stimulate hair follicles
- procyanidin, a class of flavonoid antioxidants present in apples, cinnamon, and grapes
- caffeine, which may promote cell proliferation and hair growth
The study authors also suggest trying the following alternative medicine practices, as they may help reduce stress and anxiety:
Diagnosis
 Doctors can often diagnose the cause of hair thinning from a person’s diet, preexisting medical conditions, and family history.
Doctors can often diagnose the cause of hair thinning from a person’s diet, preexisting medical conditions, and family history.Doctors can often diagnose the cause of thinning hair by looking at the pattern of hair loss.
They may ask a person about:
- their current diet
- any preexisting medical conditions
- a family history of thinning hair
- a family history of medical conditions that can cause thinning hair
A doctor may send hair or scalp samples to a laboratory for further testing. In some cases, they may order blood tests to rule out autoimmune conditions.
When to see a doctor
In most cases, thinning hair is not linked with overall health problems. If a person is concerned about hair loss, or if it affects their mental well-being, they can see a doctor.
If a person loses a lot of hair with no known cause, they should see their doctor. This is especially important if they have recently made dietary changes or started taking supplements.
The doctor may recommend that a person sees a skin specialist, or dermatologist, to determine the best ways to treat thinning hair.
Outlook
As a person gets older, it is natural for their hair to lose strength and volume. In many cases, people can improve the strength and overall health of their hair using treatments and home remedies.
Using prescription medication, topical treatments, and natural remedies can help prevent or slow down hair loss. In some cases, treating an underlying condition will solve hair loss.